시작하기전에 Ubuntu의 Application/Disk 를 이용하여 disk 포멧부터 시작하고 진행하였다. (필자의 경우 4TB 16시간이상이 걸렸다)
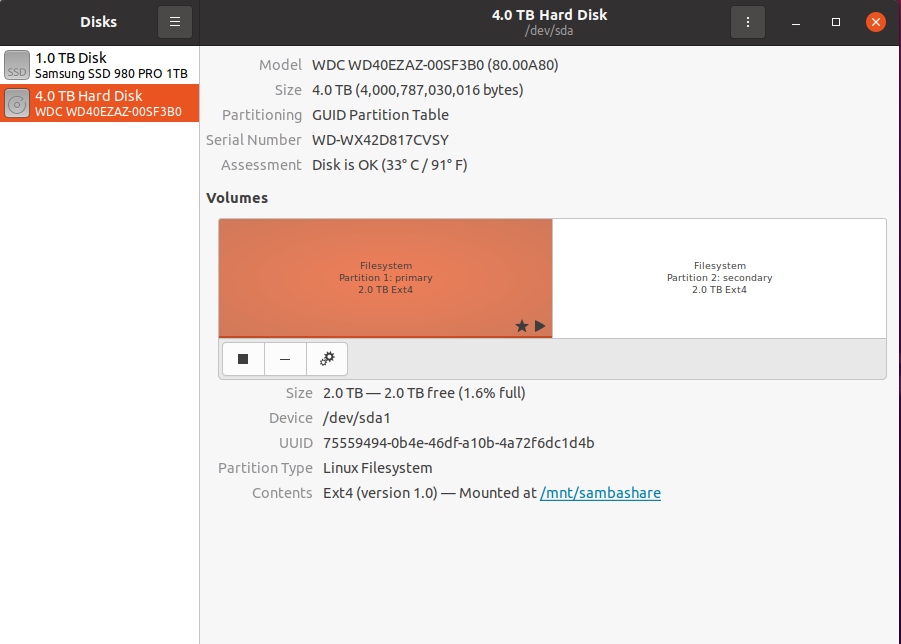
Application "Disk" in Ubuntu
1. 현재 파티션 확인하기 fdisk -l df -h
fdisk -l 를 이용하면 드라이브 목록을 확인할 수 있다.
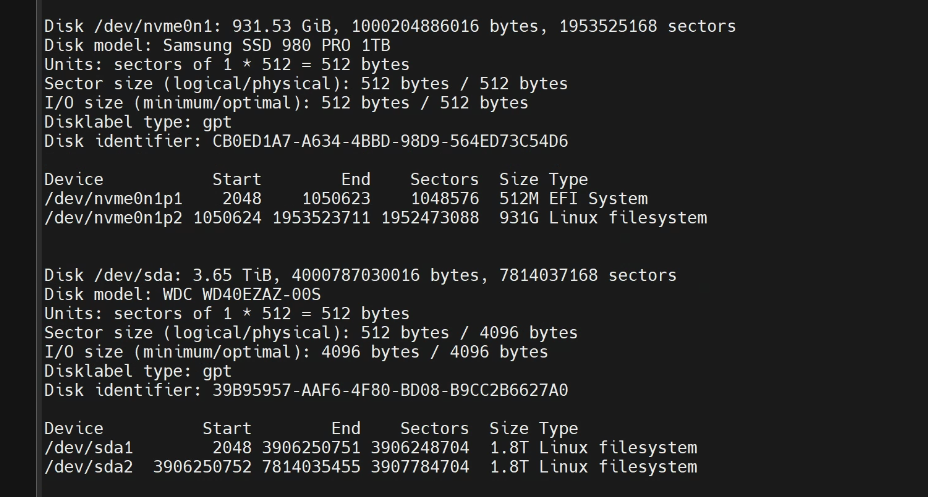
"fdisk -l", 할당을 마친 후의 드라이브 목록
할당되지 않은 상태에서는 sda1, 2가 차례로 있지 않았다. 저 부분을 파티션 할당을 해주면 된다. 리눅스는 보통 첫번째 드라이브가 /dev/sda1,2,3,… 두번째 드라이브가 /dev/sdb1,2,3… 이렇게 설정된다.
df -h 는 마운트된 폴더를 확인할 수 있다.
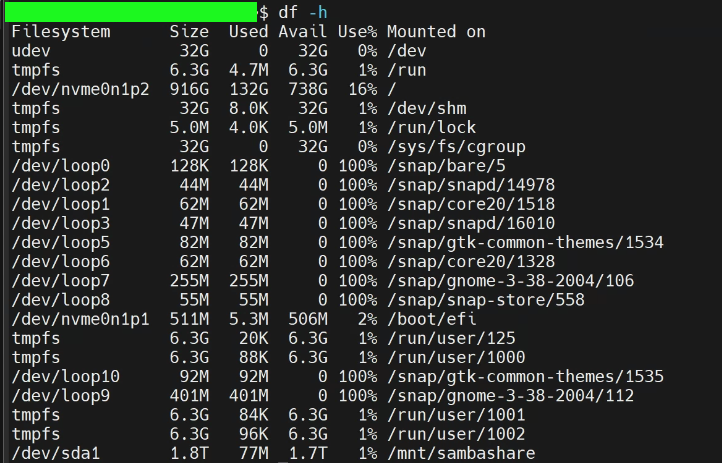
Aftering mounting the disk, confirm the allocation through "df -h"
2-1. 2TB이하 파티션 할당하기
1) fdisk/dev/[디스트명]
새로운 하드디스크를 추가한다.
-
primary partition
최대 4개까지 생성 가능하고 파티션 번호는 1-4가 있다.
-
extended partition
파일 저장용도로 사용 못하며 논리 파티션을 생성하기 위한 공간이다. 파티션 번호는 1-4가 있다.
-
logical disk
Primary partition과 같은 역할을 하며 확장 파티션 내에서만 생성 가능하다. 파티션 번호는 5~ 이며 제한 갯수는 없다.
왜 primary외에 다른 것이 있을까? 위에서 보면 알듯이 primary partition은 4개까지 밖에 파티션을 나누지 못하고 logical disk는 제한 갯수가 없다. 파티션 생성을 아래와 같이 따라가면 되겠다.
# fdisk /dev/sdb
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Device does not contain a recognized partition table
Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x6ad31b53.
WARNING: The size of this disk is 4.0 TB (4000787030016 bytes).
DOS partition table format can not be used on drives for volumes
larger than (2199023255040 bytes) for 512-byte sectors. Use parted(1) and GUID
partition table format (GPT).
The device presents a logical sector size that is smaller than
the physical sector size. Aligning to a physical sector (or optimal
I/O) size boundary is recommended, or performance may be impacted.
Command (m for help): m
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
g create a new empty GPT partition table
G create an IRIX (SGI) partition table
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended
Select (default p):p
Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1
First sector (2048-4294967295, default 2048): 2048
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-4294967294, default 4294967294): #Enter를 치면 default로 잡힌다.
Using default value 4294967294
Partition 1 of type Linux and of size 2 TiB is set
#하드디스크의 용량은 4TB이지만, 파티션에 할당할 수 있는 최대 크기는 2TB다.
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
2) mkfs -t [파일시스템] /dev/[디스크명]
파일시스템 만들기!
# mkfs -t ext4 /dev/sdb1
mke2fs 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
134217728 inodes, 536870655 blocks
26843532 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=2684354560
16384 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8192 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208,
4096000, 7962624, 11239424, 20480000, 23887872, 71663616, 78675968,
102400000, 214990848, 512000000
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
2-2. 2TB이상 파티션 할당하기
1) 2TB를 초과하는 파티션을 할당하기 위해선 parted 명령어를 사용하여 gpt 타입 파티션으로 만들어야 한다.
# parted /dev/sdb
GNU Parted 3.1
Using /dev/sdb
Welcome to GNU Parted! Type 'help' to view a list of commands.
(parted) help
align-check TYPE N check partition N for TYPE(min|opt) alignment
help [COMMAND] print general help, or help on COMMAND
mklabel,mktable LABEL-TYPE create a new disklabel (partition table)
mkpart PART-TYPE [FS-TYPE] START END make a partition
name NUMBER NAME name partition NUMBER as NAME
print [devices|free|list,all|NUMBER] display the partition table, available devices, free space, all found partitions, or a
particular partition
quit exit program
rescue START END rescue a lost partition near START and END
rm NUMBER delete partition NUMBER
select DEVICE choose the device to edit
disk_set FLAG STATE change the FLAG on selected device
disk_toggle [FLAG] toggle the state of FLAG on selected device
set NUMBER FLAG STATE change the FLAG on partition NUMBER
toggle [NUMBER [FLAG]] toggle the state of FLAG on partition NUMBER
unit UNIT set the default unit to UNIT
version display the version number and copyright information of GNU Parted
(parted) mklabel gpt
Warning: The existing disk label on /dev/sdb will be destroyed and all data on this disk will be lost. Do you want to continue?
Yes/No? yes
(parted) unit TB # 단위를 설정한다. GB or TB
(parted) mkpart primary 0.00TB 4.00TB # 용량 설정 start end
(parted) print
Model: ATA HGST HDN726040AL (scsi)
Disk /dev/sdb: 4.00TB
Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/4096B
Partition Table: gpt
Disk Flags:
Number Start End Size File system Name Flags
1 0.00TB 4.00TB 4.00TB ext4 primary # 정상적으로 추가됐다.
(parted) quit
Information: You may need to update /etc/fstab.
2) 파일 시스템을 만든다. mkfs -t ext4 /dev/sdb1
# mkfs -t ext4 /dev/sdb1
mke2fs 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
244195328 inodes, 976754176 blocks
48837708 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=3124756480
29809 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8192 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208,
4096000, 7962624, 11239424, 20480000, 23887872, 71663616, 78675968,
102400000, 214990848, 512000000, 550731776, 644972544
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
3. mount -t [파일시스템] /dev/[디스크명]
# mount -t ext4 /dev/sdb1 [path_dir_to_mount]
# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda3 20G 93M 19G 1% /
.
.
.
.
/dev/sdb1 2.0T 81M 1.9T 1% [path_dir_to_mount] # 새로 마운트한 드라이브가 보일 것이다.
이렇게 하면 4TB의 하드디스크 중에 2TB를 할당해서 사용할 수 있다.
4. fstab 파일 등록
1) 먼저 자동마운트 등록할 디스크의 UUID를 확인해야한다.
- Method 1. blkid
# blkid # 먼저 자동마운트 등록할 디스크의 UUID를 알아내야 한다. /dev/sda1: UUID="22a87868-322e-4661-af01-93b2062044ce" TYPE="xfs" . . . /dev/sdb1: UUID="e001a7f9-1154-129e-a916-dad0b54116f2" TYPE="ext4" PARTLABEL="primary" PARTUUID="52412c84-700e-2313-9e2f-c12b1ca1676a" - Method 2. (parted를 통해 등록한 경우) blkid에서 파티션한 디스크가 보이지 않음
→
vi /dev/disk/by-uuid
2) vi /etc/fstab
# vi /etc/fstab
#
# /etc/fstab
# Created by anaconda on Sat Sep 26 08:52:44 2015
#
# Accessible filesystems, by reference, are maintained under '/dev/disk'
# See man pages fstab(5), findfs(8), mount(8) and/or blkid(8) for more info
#
UUID=1c407d96-e43b-4b52-af5f-b191560e8267 / ext4 defaults 1 1
.
.
.
.
UUID=e001a7f9-1154-129e-a916-dad0b54116f2 /second ext4 defaults 1 2 # 여기에 추가한다.
3) Detail vi /etc/fstab
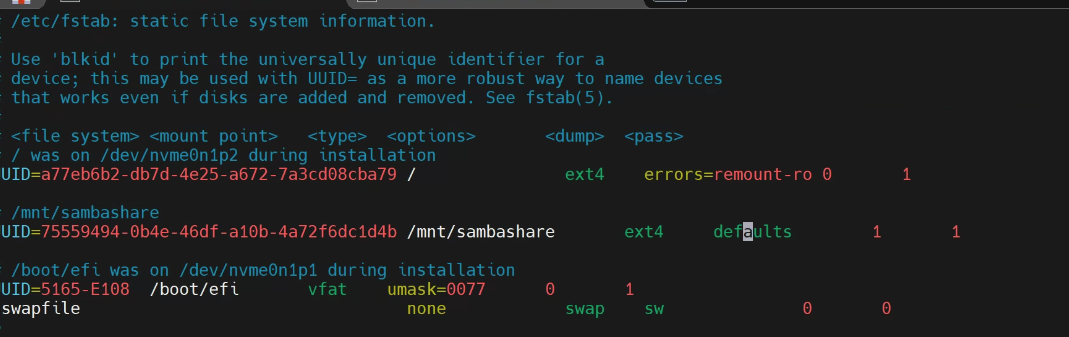
fstab 설정 값
- Reference. https://it-serial.tistory.com/entry/Linux-df-명령어-마운트-자동-등록fstab-UUID란⑤
- 마운트 정보 순서: [디스크 이름 or 디스크 UUID] [마운트 포인트] [파일 시스템] [마운트 옵션] [덤프(백업)유무] [fsck 검사 순서]
- 값들과 값들 사이에 공간은 1칸 이상만 띄우면 된다.
-
defaults 옵션
auto : 부팅시 자동으로 마운트
exec(execute) : 실행 파일을 실행할 수 있게 마운트
suid : setUID, setGID를 사용할 수 있게 마운트
rw(read, write) : r,w 권한을 가지게 마운트
nouser : 일반 유저들은 마운트 권한 없음
-
기타 옵션
ro(read only) : r 권한만 가지고 마운트
usrquota 또는 grpquota : 유저 쿼터 or 그룹 쿼터를 나눔
defaults외에 다른 옵션을 사용하고 싶을 때 “auto, exec, suid, ro” 이런식으로 분리해서 적으면 된다.
- 반대 옵션 기존 옵션에 no를 붙이기, ex. noauto, noexec
- 덤프 사용 유무, 0(사용안함) or 1(사용): 백업의 개념으로 사용한다 정도만 알고 넘어가도록 합시다.
- fsck (file system check) : 0(검사 안함), 1(1순위로 검사), 2(1순위 다음 검사) 3개로 나타냅니다. fsck명령어를 통한 파일 시스템 체크 순서를 정하는 것입니다.
- UUID (Universally Unique IDentifier) : 절대 겹치지 않는 식별자, 디스크 이름은 /dev/sdb1 같은 경우 언제든지 바뀔 수 있다.